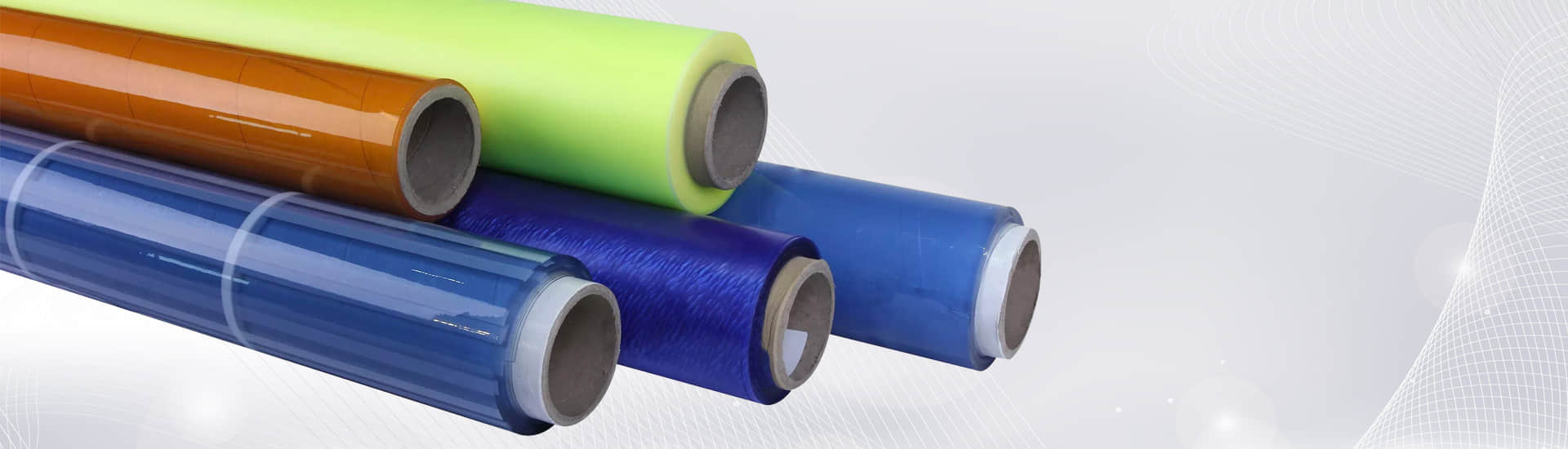
High-Temperature Resistant PVC Film
High-temperature resistant PVC film is a modified polyvinyl chloride film that significantly improves the heat resistance of traditional PVC by adopting special heat-resistant additives and polymer polymerization technology. High-temperature resistant film maintains good flexibility, chemical corrosion resistance and processing performance in long term high-temperature environments. POLYSAN high-temperature resistant PVC film complies Reach/RoHS standard, is eco-friendly plastic film.

Production Introduction
PVC film has poor high-temperature resistance, whose continuous operating temperature range is between 50°C and 60°C, with short-term tolerances of 70°C -90°C. Exceeding the limit temperature can cause softening, deformation, decomposition, discoloration, and brittleness, which impacting the lifespan of the finished product. High-temperature-resistant PVC film can typically withstand continuous operating temperatures of 90°C to 105°C and can even withstand short-term temperatures exceeding 120°C while maintaining the mechanical strength, color, and flexibility, extending the product's lifespan.
Production Parameter
Product Name | High-Temperature Resistant PVC Film |
Material | PVC Resin, High-Resistant Additives, Polymer Plasticizer |
Color | Super Clear/Normal Clear/Matte Color Customized |
Thickness | 0.05-2.5mm |
Max Width | 2000mm |
Hardness | 22-60PHR |
Working Temperature | 90°C -120°C |
Process Type | Calendering |
MOQ | 1000kgs |
Standard | EN71-3,ROHS,REACH,CA65,6P/17P/23P free, BPA free |
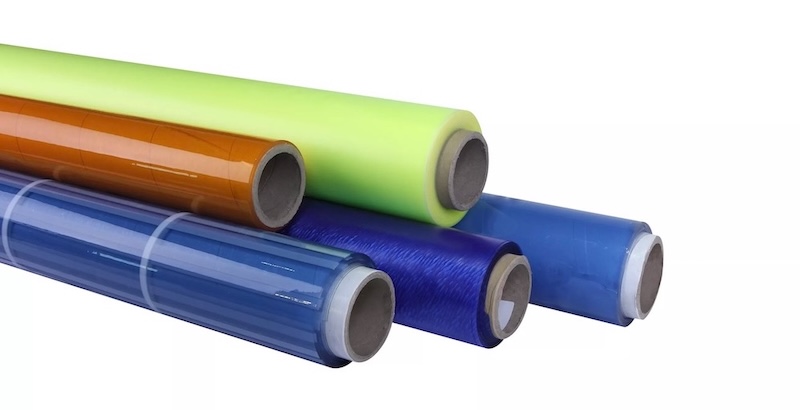

When PVC film is exposed to high temperatures, it undergoes physical and chemical changes.
1. Physical Changes
Softening and Deformation-- When temperatures exceed the glass transition temperature (Tg) and Vicat softening point, the film softens and permanently deforms under pressure.
Shrinkage--Internal stress within the film is released upon heating, resulting in dimensional shrinkage.
Yellowing--The darkening of the color is caused by the formation of polyene structures (conjugated double bonds) from the dehydrogenation of HCl.
Brittleness--Molecular chain breakage and cross-linking reactions lead to a decrease in mechanical strength and brittle film.
2. Chemical Risks
Release of HCl gas--Corrosive and irritating, harmful to equipment and human health.
Volatilization of plasticizers--Hardens the film and may pollute the environment.
Flammability--Burns at extremely high temperatures, producing large amounts of smoke and toxic gases.
The high-temperature resistance of PVC film can be adjusted through formulation.
Heat stabilizers-- the most critical additives, which effectively slow thermal degradation by absorbing HCl, replacing unstable chlorine atoms, and neutralizing free radicals.
Fillers-- calcium carbonate and talc. Appropriate amounts of fillers can provide some insulation and structural support for PVC film
Production Application
High-temperature PVC film is an ideal functional plastic film material for many high-temperature working environments.
Automotive interiors--Required to withstand summer temperatures reaching 80-90°C.
Home appliance industry--Decorative films for refrigerator door panels, washing machine control panels, air conditioner vent grilles, and water heater housings.
Packaging industry--Medical device packaging requiring high-temperature sterilization, and heat-shrink labels for food.
Architectural films-- In areas with strong sunlight, higher heat resistance is required to prevent deformation.

 English
English  Русский
Русский  Deutsch
Deutsch  Français
Français  Português
Português  Español
Español  Italiano
Italiano  العربية
العربية  한국어
한국어  Türkçe
Türkçe